Clinical proof is so important to BardyDx that it has led to three head-to-head studies.
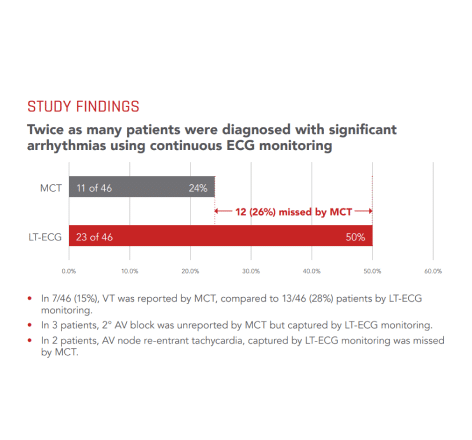
Continuous ECG monitoring versus mobile telemetry: A comparison of arrhythmia diagnostics in human- versus algorithmic-dependent systems.
Comparison of two ambulatory patch ECG monitors: The benefit of the P-wave and signal clarity.
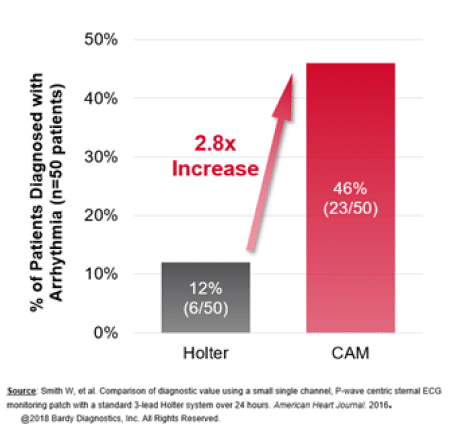
Comparison of diagnostic value using a small, single channel, P-wave centric sternal ECG monitoring patch with a standard 3-lead Holter over 24 hours.
What Healthcare Professionals are Saying
“The CAM has been an incredible step forward in rhythm monitoring for my patients and gives a much more reliable snapshot of arrhythmic risk”
-David Owens M.D.

P-wave centric patch monitors may reduce need for implantable monitors following cryptogenic stroke.
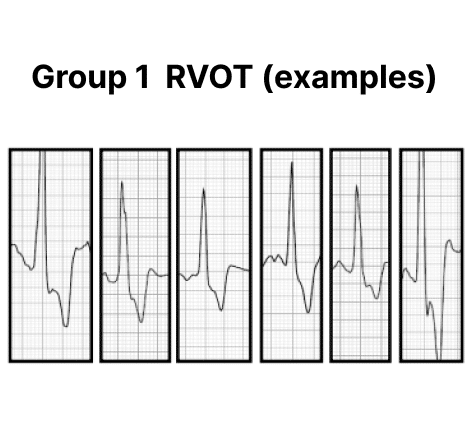
A new sternal patch ambulatory ECG monitor differentiates outflow tract PVC from non-outflow tract PVCs.
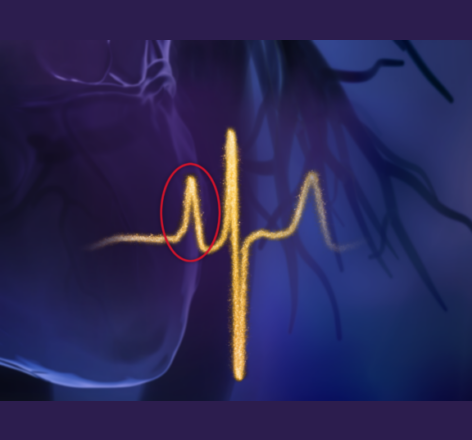
Atrial signal clarity and rhythm specificity are critical when using artificial intelligence (AI) to distinguish atrial fibrillation (AF) from rhythms that mimic AF.
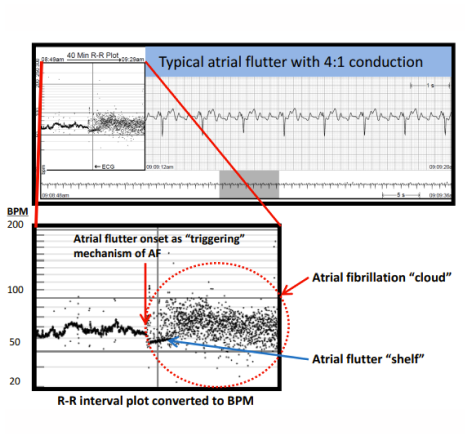
Incidence of classic atrial flutter in outpatients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation as identified with a new P-wave centric ECG monitor Implications for the AF ablation procedure.
Baxter is committed to supporting investigator-initiated research efforts to expand the body of clinical evidence related to ambulatory cardiac monitoring. If you are a U.S.-based investigator and interested in the Baxter Investigator Initiated Research Program, please go to this link: Research & Continuing Education External Funding.
US-FLC199-220022 (v5.0) 02/2025
Baxter, BardyDx, Bardy Diagnostics, BDx Design and CAM are trademarks of Baxter International Inc. or its subsidiaries.
Any other trademarks, product names or brand images appearing herein are the property of their respective owners.
© 2025 Bardy Diagnostics, Inc. All rights reserved.
Privacy | US Privacy Policy |Terms & Conditions | Intellectual Property | Cookies